Tomcat系统架构分析
1.1. Engine 容器
Engine 容器比较简单,它只定义了一些基本的关联关系,接口类图如下:
1). Engine 接口的类结构
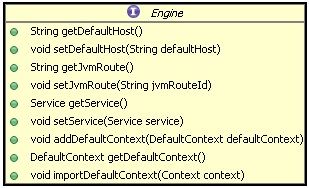
它的标准实现类是 StandardEngine,这个类注意一点就是 Engine 没有父容器了,如果调用 setParent 方法时将会报错。添加子容器也只能是 Host 类型的,代码如下:
2) StandardEngine. addChild
public void addChild(Container child) {
if (!(child instanceof Host))
throw new IllegalArgumentException
(sm.getString("standardEngine.notHost"));
super.addChild(child);
}
public void setParent(Container container) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException
(sm.getString("standardEngine.notParent"));
}
它的初始化方法也就是初始化和它相关联的组件,以及一些事件的监听。
1.1. Host 容器
Host 是 Engine 的字容器,一个 Host 在 Engine 中代表一个虚拟主机,这个虚拟主机的作用就是运行多个应用,它负责安装和展开这些应用,并且标识这个应用以便能够区分它们。它的子容器通常是 Context,它除了关联子容器外,还有就是保存一个主机应该有的信息。
1). Host 相关的类图
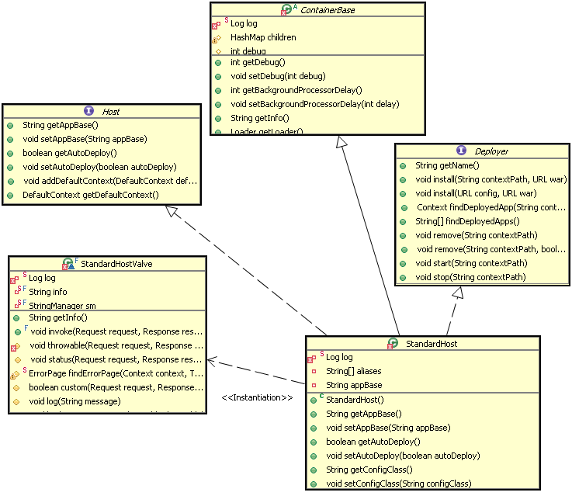
从上图中可以看出除了所有容器都继承的 ContainerBase 外,StandardHost 还实现了 Deployer 接口,上图清楚的列出了这个接口的主要方法,这些方法都是安装、展开、启动和结束每个 web application。
Deployer 接口的实现是 StandardHostDeployer,这个类实现了的最要的几个方法,Host 可以调用这些方法完成应用的部署等。
1.1. Context 容器
Context 代表 Servlet 的 Context,它具备了 Servlet 运行的基本环境,理论上只要有 Context 就能运行 Servlet 了。简单的 Tomcat 可以没有 Engine 和 Host。
Context 最重要的功能就是管理它里面的 Servlet 实例,Servlet 实例在 Context 中是以 Wrapper 出现的,还有一点就是 Context 如何才能找到正确的 Servlet 来执行它呢? Tomcat5 以前是通过一个 Mapper 类来管理的,Tomcat5 以后这个功能被移到了 request 中,在前面的时序图中就可以发现获取子容器都是通过 request 来分配的。
Context 准备 Servlet 的运行环境是在 Start 方法开始的,这个方法的代码片段如下:
1). StandardContext.start
public synchronized void start() throws LifecycleException {
………
if( !initialized ) {
try {
init();
} catch( Exception ex ) {
throw new LifecycleException("Error initializaing ", ex);
}
}
………
lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(BEFORE_START_EVENT, null);
setAvailable(false);
setConfigured(false);
boolean ok = true;
File configBase = getConfigBase();
if (configBase != null) {
if (getConfigFile() == null) {
File file = new File(configBase, getDefaultConfigFile());
setConfigFile(file.getPath());
try {
File appBaseFile = new File(getAppBase());
if (!appBaseFile.isAbsolute()) {
appBaseFile = new File(engineBase(), getAppBase());
}
String appBase = appBaseFile.getCanonicalPath();
String basePath =
(new File(getBasePath())).getCanonicalPath();
if (!basePath.startsWith(appBase)) {
Server server = ServerFactory.getServer();
((StandardServer) server).storeContext(this);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("Error storing config file", e);
}
} else {
try {
String canConfigFile = (new File(getConfigFile())).getCanonicalPath();
if (!canConfigFile.startsWith (configBase.getCanonicalPath())) {
File file = new File(configBase, getDefaultConfigFile());
if (copy(new File(canConfigFile), file)) {
setConfigFile(file.getPath());
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("Error setting config file", e);
}
}
}
………
Container children[] = findChildren();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
if (children[i] instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) children[i]).start();
}
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
………
}
它主要是设置各种资源属性和管理组件,还有非常重要的就是启动子容器和 Pipeline。
我们知道 Context 的配置文件中有个 reloadable 属性,如下面配置:
2). Server.xml
<Context
path="/library"
docBase="D:\projects\library\deploy\target\library.war"
reloadable="true"
/>
当这个 reloadable 设为 true 时,war 被修改后 Tomcat 会自动的重新加载这个应用。如何做到这点的呢 ? 这个功能是在 StandardContext 的 backgroundProcess 方法中实现的,这个方法的代码如下:
3). StandardContext. backgroundProcess
public void backgroundProcess() {
if (!started) return;
count = (count + 1) % managerChecksFrequency;
if ((getManager() != null) && (count == 0)) {
try {
getManager().backgroundProcess();
} catch ( Exception x ) {
log.warn("Unable to perform background process on manager",x);
}
}
if (getLoader() != null) {
if (reloadable && (getLoader().modified())) {
try {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader
(StandardContext.class.getClassLoader());
reload();
} finally {
if (getLoader() != null) {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader
(getLoader().getClassLoader());
}
}
}
if (getLoader() instanceof WebappLoader) {
((WebappLoader) getLoader()).closeJARs(false);
}
}
}
它会调用 reload 方法,而 reload 方法会先调用 stop 方法然后再调用 Start 方法,完成 Context 的一次重新加载。可以看出执行 reload 方法的条件是 reloadable 为 true 和应用被修改,那么这个 backgroundProcess 方法是怎么被调用的呢?
这个方法是在 ContainerBase 类中定义的内部类 ContainerBackgroundProcessor 被周期调用的,这个类是运行在一个后台线程中,它会周期的执行 run 方法,它的 run 方法会周期调用所有容器的 backgroundProcess 方法,因为所有容器都会继承 ContainerBase 类,所以所有容器都能够在 backgroundProcess 方法中定义周期执行的事件。
本教程由尚硅谷教育大数据研究院出品,如需转载请注明来源,欢迎大家关注尚硅谷公众号(atguigu)了解更多。


