Java常用API(五)
9.6 字符串
java.lang.String 类代表字符串。Java语言提供对象字符串的特殊支持:
- Java程序中所有的字符串文字(例如
"abc")都可以被看作是实现此类的实例,即所有""引起来的内容都是字符串对象。 - Java语言提供对字符串串联符号(
+),即Java重载了+的功能。 - Java语言提供了将任意类型对象转换为字符串的特殊支持(
toString()方法)。
9.6.1 字符串的特点
- 字符串
String类型本身是final声明的,意味着我们不能继承String。 String对象内部是用字符数组进行保存的JDK8的
String内部是用字符数组进行保存的private final char[] value;"abc"等效于char[] data={ 'a', 'b', 'c' }。例如: String str = "abc"; 相当于: char data[] = {'a', 'b', 'c'}; String str = new String(data); // String底层是靠字符数组实现的。JDK9之后
String内部是用byte数组进行保存的private final byte[] value; private final byte coder;//新增加的字段,表示字符串采用的编码 1是UTF-16BE,0是LATIN1定义的字符串中,如果没有汉字,每个字符将采用
LATIN1编码表存储,如果字符串中包含汉字等非ASCII码表的字符,存储的编码就是UTF-16BE,相比JDK1.8节约内存。
- 字符串的对象也是不可变对象,意味着一旦进行修改,就会产生新对象。
为什么
String对象不可变?或者说String类是如何设计为对象不可变的?(面试题)String类中value数组是final修饰的,意味着这个数组地址不可变,即不能对同一个String对象的value数组进行扩容、缩容等。- 虽然
final修饰的value数组元素值可以修改。但是由于它是private修饰,外部不能直接操作它,所以在String类外无法直接修改value数组的元素值(除非用反射)。 String类型中提供的所有方法实现涉及到value数组长度需要变化,或value元素值需要变化,都是用新对象来表示修改后内容的。
综上3点保证了
String对象的不可变。- 既然
String对象不可变,那么我们“修改”String对象要如何操作?- 我们修改了字符串后,如果想要获得新的内容,必须重新接收。
- 如果程序中涉及到大量的字符串的修改操作,那么此时的时空消耗比较高。可能需要考虑使用
StringBuilder或StringBuffer的可变字符序列。
就因为字符串对象设计为不可变,所以可以共享。Java中把需要共享的字符串常量对象放在字符串常量池中。
String s1 = "abc"; String s2 = "abc"; System.out.println(s1 == s2); // 内存中只有一个"abc"对象被创建,同时被s1和s2共享。
9.6.2 API方法
1、构造字符串对象
除了直接 "" 构建字符串之外,还可以通过以下4个方式:构造器、valueOf 方法、+、toString 方法
使用构造方法
public String():初始化新创建的String对象,以使其表示空字符序列。String(String original): 初始化一个新创建的String对象,使其表示一个与参数相同的字符序列;换句话说,新创建的字符串是该参数字符串的副本。public String(char[] value):通过当前参数中的字符数组来构造新的String。public String(char[] value,int offset, int count):通过字符数组的一部分来构造新的String。public String(byte[] bytes):通过使用平台的默认字符集解码当前参数中的字节数组来构造新的String。public String(byte[] bytes,String charsetName):通过使用指定的字符集解码当前参数中的字节数组来构造新的String。
构造举例,代码如下:
//字符串常量对象 String str = "hello"; // 无参构造 String str1 = new String(); //创建"hello"字符串常量的副本 String str2 = new String("hello"); //通过字符数组构造 char chars[] = {'a', 'b', 'c','d','e'}; String str3 = new String(chars); String str4 = new String(chars,0,3); // 通过字节数组构造 byte bytes[] = {97, 98, 99 }; String str5 = new String(bytes); String str6 = new String(bytes,"GBK");使用静态方法
valueOf和copyValueOfstatic String copyValueOf(char[] data): 返回指定数组中表示该字符序列的Stringstatic String copyValueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count):返回指定数组中表示该字符序列的Stringstatic String valueOf(char[] data): 返回指定数组中表示该字符序列的Stringstatic String valueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count): 返回指定数组中表示该字符序列的Stringstatic String valueOf(xx value):xx支持各种数据类型,返回各种数据类型的value参数的字符串表示形式。
public static void main(String[] args) { char[] data = {'h','e','l','l','o','j','a','v','a'}; String s1 = String.copyValueOf(data); String s2 = String.copyValueOf(data,0,5); int num = 123456; String s3 = String.valueOf(num); System.out.println(s1); System.out.println(s2); System.out.println(s3); }任意类型与字符串
+任意数据类型与
"字符串"进行拼接,结果都是字符串类型public static void main(String[] args) { int num = 123456; String s = num + ""; System.out.println(s); Student stu = new Student(); String s2 = stu + "";//自动调用对象的toString(),然后与""进行拼接 System.out.println(s2); }任意对象.
toStringObject类中声明了
toString()方法,因此任意对象都可以调用toString方法,转为字符串类型。如果没有重写toString的话,返回的默认是“对象的运行时类型@对象的hashCode值的十六进制值”public static void main(String[] args) { LocalDate today = LocalDate.now(); String str = today.toString(); System.out.println(str); }
2、求字符串的长度
int length():返回字符串的长度@Test public void test1(){ System.out.println("hello".length()); }
3、转大小写
String toLowerCase():将字符串中大写字母转为小写String toUpperCase():将字符串中小写字母转为大写
@Test
public void test2(){
System.out.println("Hello".toLowerCase());
System.out.println("Hello".toUpperCase());
}
4、字符串对象的比较
涉及到以下5个方式方法:==、equals、equalsIgnoreCase、compareTo、compareToIgnoreCase、Collator
====运算符:比较是两个字符串对象的地址@Test public void test1(){ String str1 = "hello"; String str2 = "hello"; System.out.println(str1 == str2);//true,说明str1和str2指向同一个字符串对象 String str3 = new String("hello"); String str4 = new String("hello"); System.out.println(str1 == str4); //false System.out.println(str3 == str4); //false }equals方法比较boolean equals(Object obj)方法:比较是两个字符串对象的内容,因为String类型重写equals,equals方法比较字符串内容时严格区分大小写。@Test public void test2(){ String str1 = "hello"; String str2 = "hello"; System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));//true String str3 = new String("hello"); String str4 = new String("hello"); System.out.println(str1.equals(str3));//true System.out.println(str3.equals(str4));//true }equalsIgnoreCase方法boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str)方法:比较是两个字符串对象的内容,并且不区分大小写。@Test public void test3(){ String str1 = new String("hello"); String str2 = new String("HELLO"); System.out.println(str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str2)); //true } @Test public void test04(){ //随机生成验证码,验证码由0-9,A-Z,a-z的4位字符组成 char[] array = new char[26*2+10]; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { array[i] = (char)('0' + i); } for (int i = 10,j=0; i < 10+26; i++,j++) { array[i] = (char)('A' + j); } for (int i = 10+26,j=0; i < array.length; i++,j++) { array[i] = (char)('a' + j); } char[] code = new char[4]; Random rand = new Random(); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { code[i]= array[rand.nextInt(array.length)]; } String codeString = new String(code); System.out.println("验证码:" + codeString); //将用户输入的单词全部转为小写,如果用户没有输入单词,重新输入 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("请输入验证码:"); String inputCode = input.nextLine(); if(!codeString.equalsIgnoreCase(inputCode)){ System.out.println("验证码输入不正确"); }else{ System.out.println("验证码输入正确"); } input.close(); }compareTo方法int compareTo(String str)方法:String类型实现了java.lang.Comparable接口,重写了Comparable接口的抽象方法,即String对象支持自然排序,该方法按照字符的Unicode编码值进行比较大小的,严格区分大小写。@Test public void test5(){ String str1 = "hello"; String str2 = "world"; String str3 = "HELLO"; System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2));//-15 System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str3));//32 } @Test public void test6(){ String[] arr = {"hello","java","chai","Jack","hi"}; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); Arrays.sort(arr); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); }compareToIgnoreCase方法int compareToIgnoreCase(String str):String类型支持不区分大小写比较字符串大小。具体原理是先统一大小写再比较大小。@Test public void test7(){ String str1 = "hello"; String str2 = "world"; String str3 = "HELLO"; System.out.println(str1.compareToIgnoreCase(str2));//-15 System.out.println(str1.compareToIgnoreCase(str3));//0 } @Test public void test8(){ String[] arr = {"hello","java","chai","Jack","Hi"}; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator() { @Override public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) { String s1 = (String) o1; String s2 = (String) o2; return s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2); } }); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); }区分语言环境的
String比较java.text.Collator类执行区分语言环境的String比较。@Test public void test9(){ String[] arr = {"张三","李四","柴林燕","王五","尚硅谷"}; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator() { @Override public int compare(Object o1 , Object o2) { String s1 = (String) o1; String s2 = (String) o2; Collator collator = Collator.getInstance(Locale.CHINA); return collator.compare(s1,s2); } }); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); }
5、去掉前后空白
String trim():去掉字符串前后空白符@Test public void test3(){ System.out.println("[" + " hello world ".trim() + "]"); } @Test public void test04(){ //将用户输入的单词转为小写,如果用户没有输入单词,重新输入 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String word; while(true){ System.out.print("请输入单词:"); word = input.nextLine(); if(word.trim().length()!=0){ word = word.toLowerCase(); break; } } System.out.println("你输入的单词是:" + word); input.close(); }
6、空字符串的判断
isEmpty()isBlank()@Test public void test3()throws Exception{ String s = ""; System.out.println(s.isEmpty()); System.out.println(s.length()==0); System.out.println(s.equals("")); System.out.println("".equals("")); System.out.println(s.isBlank()); System.out.println(s.trim().length()==0); }
7、字符串开头与结尾的判断
boolean startsWith(xx):是否以xx开头@Test public void test4(){ String name = "张三"; System.out.println(name.startsWith("张")); }boolean endsWith(xx):是否以xx结尾@Test public void test5(){ String file = "Hello.txt"; if(file.endsWith(".java")){ System.out.println("Java源文件"); }else if(file.endsWith(".class")){ System.out.println("Java字节码文件"); }else{ System.out.println("其他文件"); } }
8、字符串内容查找
boolean contains(xx):是否包含xxint indexOf(xx):从前往后找当前字符串中xx,即如果有返回第一次出现的下标,要是没有返回-1int lastIndexOf(xx):从后往前找当前字符串中xx,即如果有返回最后一次出现的下标,要是没有返回-1@Test public void test05(){ String str = "尚硅谷是一家靠谱的培训机构,尚硅谷可以说是IT培训的小清华,JavaEE是尚硅谷的当家学科,尚硅谷的大数据培训是行业独角兽。尚硅谷的前端和运维专业一样独领风骚。"; System.out.println("是否包含清华:" + str.contains("清华")); System.out.println("培训出现的第一次下标:" + str.indexOf("培训")); System.out.println("培训出现的最后一次下标:" + str.lastIndexOf("培训")); }
9、字符串截取
String substring(int beginIndex):返回一个新的字符串,它是此字符串的从beginIndex开始截取到最后的一个子字符串。String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex):返回一个新字符串,它是此字符串从beginIndex开始截取到endIndex(不包含)的一个子字符串。@Test public void test06(){ String str = "helloworldjavaatguigu"; String sub1 = str.substring(5); String sub2 = str.substring(5,10); System.out.println(sub1); System.out.println(sub2); } @Test public void test07(){ String fileName = "快速学习Java的秘诀.dat"; //截取文件名 System.out.println("文件名:" + fileName.substring(0,fileName.lastIndexOf("."))); //截取后缀名 System.out.println("后缀名:" + fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("."))); }
10、获取char和char[]
char charAt(index):返回[index]位置的字符char[] toCharArray(): 将此字符串转换为一个新的字符数组返回将字符数组转为
String对象,可以使用之前介绍过的构造器和静态方法valueOf或copyValueOf等String(char[] value):返回指定数组中表示该字符序列的String。String(char[] value, int offset, int count):返回指定数组中表示该字符序列的String。static String copyValueOf(char[] data): 返回指定数组中表示该字符序列的Stringstatic String copyValueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count):返回指定数组中表示该字符序列的Stringstatic String valueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count): 返回指定数组中表示该字符序列的Stringstatic String valueOf(char[] data):返回指定数组中表示该字符序列的String
@Test public void test08(){ //将字符串中的字符按照大小顺序排列 String str = "helloworldjavaatguigu"; char[] array = str.toCharArray(); Arrays.sort(array); str = new String(array); System.out.println(str); } @Test public void test09(){ //将首字母转为大写 String str = "jack"; str = Character.toUpperCase(str.charAt(0))+str.substring(1); System.out.println(str); }
11、字符串的编码与解码
byte[] getBytes():编码,把字符串变为字节数组,按照平台默认的字符编码方式进行编码byte[] getBytes(字符编码方式):按照指定的编码方式进行编码new String(byte[] )或new String(byte[], int, int):解码,按照平台默认的字符编码进行解码new String(byte[],字符编码方式 )或new String(byte[], int, int,字符编码方式):解码,按照指定的编码方式进行解码==(编码方式见附录10.7.1)==

@Test public void test10()throws Exception{ byte[] data = {(byte)0B01100001, (byte)0B01100010, (byte)0B01100011, (byte)0B01100100}; System.out.println(new String(data,"ISO8859-1")); System.out.println(new String(data,"GBK")); System.out.println(new String(data,"UTF-8")); } @Test public void test11()throws Exception{ byte[] data = {(byte)0B01100001, (byte)0B01100010, (byte)0B01100011,(byte)0B11001001,(byte)0B11010000}; System.out.println(new String(data,"ISO8859-1")); System.out.println(new String(data,"GBK")); System.out.println(new String(data,"UTF-8")); } @Test public void test12()throws Exception{ byte[] data = {(byte)0B01100001,(byte)0B11100101, (byte)0B10110000, (byte)0B10011010, (byte)0B11000111, (byte)0B10101011}; System.out.println(new String(data,"ISO8859-1")); System.out.println(new String(data,"GBK")); System.out.println(new String(data,"UTF-8")); } @Test public void test13() throws Exception { String str = "中国"; System.out.println(str.getBytes("ISO8859-1").length);// 2 // ISO8859-1把所有的字符都当做一个byte处理,处理不了多个字节 System.out.println(str.getBytes("GBK").length);// 4 每一个中文都是对应2个字节 System.out.println(str.getBytes("UTF-8").length);// 6 常规的中文都是3个字节 /* * 不乱码:(1)保证编码与解码的字符集名称一样(2)不缺字节 */ System.out.println(new String(str.getBytes("ISO8859-1"), "ISO8859-1"));// 乱码 System.out.println(new String(str.getBytes("GBK"), "GBK"));// 中国 System.out.println(new String(str.getBytes("UTF-8"), "UTF-8"));// 中国 }
12、字符串匹配正则表达式
boolean matches(正则表达式):判断当前字符串是否匹配某个正则表达式。==(正则表达式详细见附录)==@Test public void test16(){ //简单判断是否全部是数字,这个数字可以是1~n位 String str = "12a345"; //正则不是Java的语法,它是独立与Java的规则 //在正则中\是表示转义, //同时在Java中\也是转义 boolean flag = str.matches("\\d+"); System.out.println(flag); } @Test public void test17(){ String str = "123456789"; //判断它是否全部由数字组成,并且第1位不能是0,长度为9位 //第一位不能是0,那么数字[1-9] //接下来8位的数字,那么[0-9]{8}+ boolean flag = str.matches("[1-9][0-9]{8}+"); System.out.println(flag); } @Test public void test18(){ //密码要求:必须有大写字母,小写字母,数字组成,6位 System.out.println("Cly892".matches("^(?=.*[A-Z])(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[0-9])[A-Za-z0-9]{6}$"));//true System.out.println("1A2c45".matches("^(?=.*[A-Z])(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[0-9])[A-Za-z0-9]{6}$"));//true System.out.println("Clyyyy".matches("^(?=.*[A-Z])(?=.*[0-9])[A-Za-z0-9]{6}$"));//false /* (1)密码的长度为6,且只能有[A-Za-z0-9]组成。 (2)另外,三个非捕获组都能匹配到自己的值。 (?=.*[A-Z]):匹配值 C (?=.*[a-z]):匹配值 Clyya (?=.*[0-9]):匹配值 Clyya1 三个非捕获组都有值,即都匹配上了就行。 非捕获组是只匹配不捕获。 */ }
13、字符串内容的替换
String replace(xx,xx):不支持正则String replaceFirst(正则,value):替换第一个匹配部分String replaceAll(正则, value):替换所有匹配部分@Test public void test19(){ String str = "hello244world.java;887"; String s1 = str.replace("244",""); System.out.println("s1 = " + s1); String s2 = str.replaceFirst("\\d+",""); System.out.println("s2 = " + s2); //把其中的非字母去掉 String s3 = str.replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z]", ""); System.out.println("s3 = " + s3); }
14、字符串拆分
String[] split(正则):按照某种规则进行拆分@Test public void test20(){ String str = "Hello World java atguigu"; String[] all = str.split(" "); for (int i = 0; i < all.length; i++) { System.out.println(all[i]); } } @Test public void test21(){ String str = "1Hello2World3java4atguigu"; str = str.replaceFirst("\\d", ""); System.out.println(str); String[] all = str.split("\\d"); for (int i = 0; i < all.length; i++) { System.out.println(all[i]); } } @Test public void test23(){ String str = "张三.23|李四.24|王五.25"; //|在正则中是有特殊意义,我这里要把它当做普通的| String[] all = str.split("\\|"); //转成一个一个学生对象 Student[] students = new Student[all.length]; for (int i = 0; i < students.length; i++) { //.在正则中是特殊意义,我这里想要表示普通的. String[] strings = all[i].split("\\.");//张三, 23 String name = strings[0]; int age = Integer.parseInt(strings[1]); students[i] = new Student(name,age); } for (int i = 0; i < students.length; i++) { System.out.println(students[i]); } }class Student { private String name; private int age; public Student(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }
15、字符串拼接方法
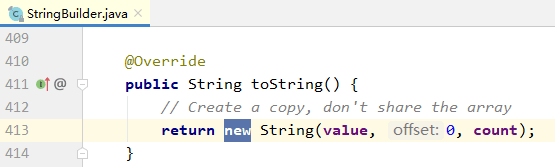
两种方式: 字符串1.concat(字符串2):只要拼接的不是空字符串,每次都new一个String 字符串1 + 字符串2: ""常量拼接,编译器直接优化为拼接后的字符串常量值 非""常量拼接,编译器优化为StringBuilder的append,然后再把结果toString。
package com.atguigu.string;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestStringConcat {
@Test
public void test1(){
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "world";
String s3 = s1 + s2;
String s4 = s1.concat(s2);
System.out.println("s3 = " + s3);//helloworld
System.out.println("s4 = " + s4);//helloworld
}
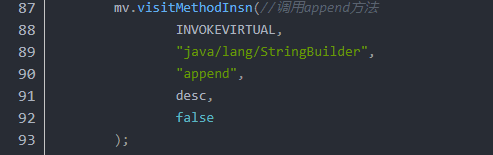
}
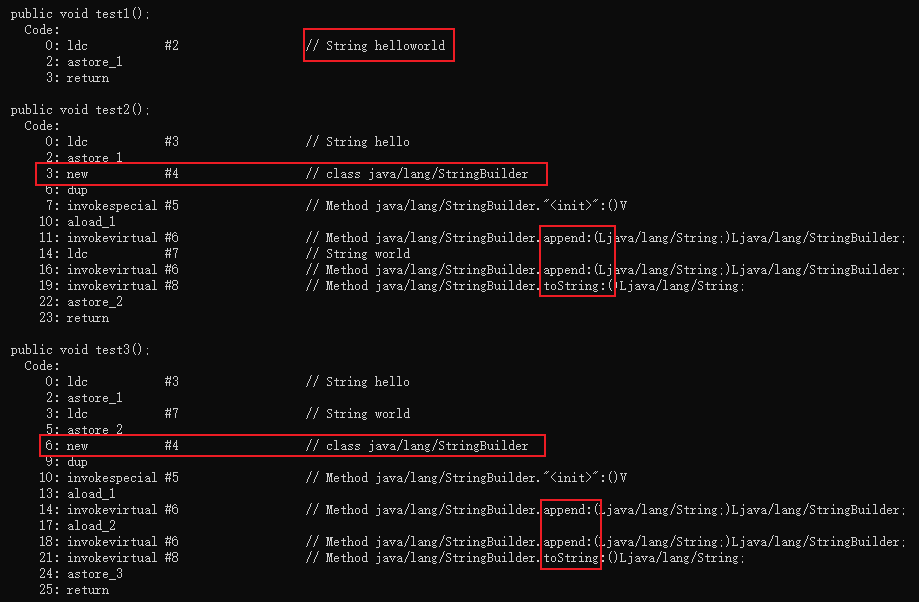
class Test{
public void test1() {
String s1 = "hello" + "world";
}
public void test2() {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = s1 + "world";
}
public void test3() {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "world";
String s3 = s1 + s2;
}
}
JDK1.9及以后的版本看到的是
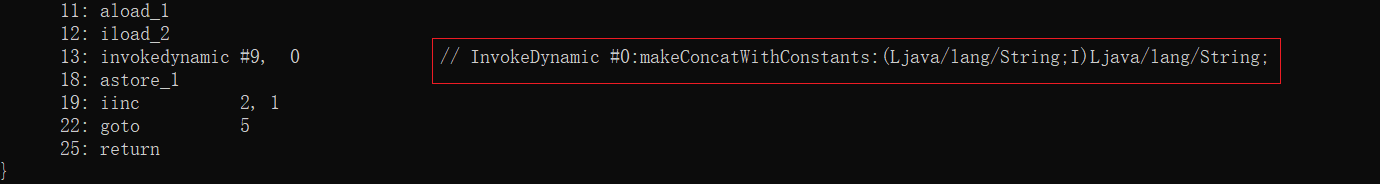
动态指令invokedynamic指令会调用makeConcatWithConstants方法进行字符串的连接。该方法位于java.lang.invoke.StringConcatFactory类中,如果继续往下跟踪,最终还是调用StringBuilder类append方法,篇幅有限,就不一一展示了: