Java中的集合(上)
第11章 集合
本章学习目标
- 知道集合与数组的区别
- 掌握Collection接口的常用方法
- 理解HashSet、LinkedHashSet、TreeSet的区别
- 理解Set与List集合的区别
- 掌握List接口的常用方法
- 理解Vector和ArrayList的区别
- 理解ArrayList与LinkedList的区别
- 掌握Queue和Deque队列接口的常用方法
- 掌握栈和队列的区别
- 知道Collection集合与Map集合的区别
- 掌握Map接口的常用方法
- 掌握Hashtable与HashMap的区别
- 掌握LinkedHashMap、TreeMap、Properties的区别
- 了解Set与Map之间的关系
- 掌握集合工具类Collections的常用方法
- 掌握数组与List集合之间的转换
- 掌握集合框架关系图
11.1 Collection集合
11.1.1 集合的概念
集合是java中提供的一种容器,可以用来存储多个数据。
集合和数组既然都是容器,它们有啥区别呢?
- 数组的长度是固定的。集合的长度是可变的。
- 数组中可以存储基本数据类型值,也可以存储对象,而集合中只能存储对象
集合主要分为两大系列:Collection和Map,Collection 表示一组对象,Map表示一组映射关系或键值对。
11.1.2 Collection<E>接口
Collection 层次结构中的根接口。Collection 表示一组对象,这些对象也称为 collection 的元素。一些 collection 允许有重复的元素,而另一些则不允许。一些 collection 是有序的,而另一些则是无序的。JDK 不提供此接口的任何直接实现:它提供更具体的子接口(如 Set 和 List、Queue)实现。此接口通常用来传递 collection,并在需要最大普遍性的地方操作这些 collection。
Collection<E>是所有单列集合的父接口,因此在Collection中定义了单列集合(List和Set)通用的一些方法,这些方法可用于操作所有的单列集合。方法如下:
1、添加元素
- (1)add(E obj):添加元素对象到当前集合中
- (2)addAll(Collection<? extends E> other):添加other集合中的所有元素对象到当前集合中,即this = this ∪ other
2、删除元素
- (1) boolean remove(Object obj) :从当前集合中删除第一个找到的与obj对象equals返回true的元素。
- (2)boolean removeAll(Collection<?> coll):从当前集合中删除所有与coll集合中相同的元素。即this = this - this ∩ coll
- (3)boolean retainAll(Collection<?> coll):从当前集合中删除两个集合中不同的元素,使得当前集合仅保留与c集合中的元素相同的元素,即当前集合中仅保留两个集合的交集,即this = this ∩ coll;
- (4)void clear():清空集合
- (5)boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) :删除满足给定条件的此集合的所有元素。removeIf方法是**Java8**引入的。
3、查询与获取元素
- (1)boolean isEmpty():判断当前集合是否为空集合。
- (2)boolean contains(Object obj):判断当前集合中是否存在一个与obj对象equals返回true的元素。
- (3)boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c):判断c集合中的元素是否在当前集合中都存在。即c集合是否是当前集合的“子集”。
- (4)int size():获取当前集合中实际存储的元素个数
- (5)Object[] toArray():返回包含当前集合中所有元素的数组
- (6)T[] toArray(T[] arr):返回包含当前集合中所有元素的数组
4、遍历集合
- (1)default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action)
- (2)foreach循环。
所有实现了java.lang.Iterable接口的集合都支持foreach循环。而Collection接口就继承了Iterable接口。
5、示例代码
package com.atguigu.collection;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class TestCollection {
@Test
public void test1(){
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>();
coll.add("hello");
coll.add("java");
coll.add("world");
System.out.println(coll);
}
@Test
public void test2(){
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>();
coll.add("hello");
coll.add("java");
coll.add("world");
System.out.println(coll);
Collection<String> other = new ArrayList<>();
other.add("尚硅谷");
other.add("JavaEE");
other.add("大数据");
other.add("嵌入式");
other.add("鸿蒙");
coll.addAll(other);
System.out.println(coll);
}
@Test
public void test3(){
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>();
coll.add("hello");
coll.add("java");
coll.add("world");
coll.add("atguigu");
coll.add("chai");
coll.remove("java");
System.out.println(coll);
Predicate<String> p = new Predicate<String>() {
@Override
public boolean test(String s) {
return s.contains("a");
}
};
coll.removeIf(p);
System.out.println(coll);
Collection<String> other = new ArrayList<>();
other.add("尚硅谷");
other.add("JavaEE");
other.add("world");
other.add("hello");
coll.removeAll(other);
System.out.println(coll);
}
@Test
public void test4() {
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>();
coll.add("hello");
coll.add("java");
coll.add("world");
coll.add("atguigu");
coll.add("chai");
Collection<String> other = new ArrayList<>();
other.add("尚硅谷");
other.add("JavaEE");
other.add("world");
other.add("hello");
coll.retainAll(other);
System.out.println(coll);
}
@Test
public void test5() {
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>();
coll.add("hello");
coll.add("java");
coll.add("world");
coll.add("atguigu");
coll.add("chai");
System.out.println(coll.isEmpty());
System.out.println(coll.size());
System.out.println(coll.contains("java"));
Collection<String> other = new ArrayList<>();
other.add("尚硅谷");
other.add("JavaEE");
other.add("world");
other.add("hello");
System.out.println(coll.containsAll(other));
}
@Test
public void test6() {
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>();
coll.add("hello");
coll.add("java");
coll.add("world");
coll.add("atguigu");
coll.add("chai");
Object[] objects = coll.toArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(objects));
String[] strings = new String[0];
strings = coll.toArray(strings);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strings));
}
@Test
public void test7() {
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>();
coll.add("hello");
coll.add("java");
coll.add("world");
coll.add("atguigu");
coll.add("chai");
Consumer<String> c = new Consumer<String>() {
@Override
public void accept(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
};
coll.forEach(c);
}
@Test
public void test8() {
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>();
coll.add("hello");
coll.add("java");
coll.add("world");
coll.add("atguigu");
coll.add("chai");
for (String s : coll) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
11.2 Set集合
11.2.1 Set接口介绍
`Set`接口是`Collection`的子接口,set接口没有提供额外需要实现类实现的抽象方法。但是比`Collection`接口更加严格了。
Set 集合不允许包含相同的元素,即元素不可重复。
Set的常用实现类有:`HashSet`、`TreeSet`、`LinkedHashSet`等。
package com.atguigu.list;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class TestSet {
@Test
public void test03(){
LinkedHashSet<String> set = new LinkedHashSet<>();//按照添加顺序,不可重复
set.add("hello");
set.add("java");
set.add("hello");
set.add("java");
System.out.println(set);
}
@Test
public void test02(){
TreeSet<String> set = new TreeSet<>();//有大小顺序,不可重复
set.add("hello");
set.add("java");
set.add("hello");
set.add("java");
System.out.println(set);
}
@Test
public void test01(){
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();//无序,不可重复
set.add("hello");
set.add("java");
set.add("hello");
set.add("java");
System.out.println(set);
}
}
11.2.2 元素相等和重复问题
- HashSet和LinkedHashSet元素不可重复是依赖于equals和hashCode方法
package com.atguigu.set;
public class Circle {
private double radius;
public Circle(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Circle{" +
"radius=" + radius +
'"}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass()!= o.getClass()) return false;
Circle circle = (Circle) o;
return Double.compare(circle.radius, radius) == 0;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
long temp = Double.doubleToLongBits(radius);
return (int) (temp ^ (temp >>> 32));
}
}
@Test
public void test08(){
HashSet<Circle> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(new Circle(1));
set.add(new Circle(1));
System.out.println(set);
}
- TreeSet元素不可重复是依赖于比较器的compareTo或compare方法
package com.atguigu.set;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.text.Collator;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class TestTreeSet {
@Test
public void test1(){
//String类实现Comparable,所以String类的对象可以方法TreeSet中,默认按照字符的编码值排序
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet();
treeSet.add("hello");
treeSet.add("java");
treeSet.add("haha");
treeSet.add("world");
treeSet.add("heihei");
System.out.println(treeSet);
//[haha, heihei, hello, java, world]
}
@Test
public void test2(){
//使用String类的定制比较器,按照中文的拼音顺序
Collator collator = Collator.getInstance(Locale.CHINA);//得到一个实现了Comparator接口的字符串定制比较器
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet(collator);
treeSet.add("张三");
treeSet.add("李四");
treeSet.add("王五");
treeSet.add("赵六");
System.out.println(treeSet);
//[李四, 王五, 张三, 赵六]
//li wang zhang zhao
}
@Test
public void test3(){
//使用String类的定制比较器,按照字符串的长短
Comparator lengthComparator = new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
String s1 = (String) o1;
String s2 = (String) o2;
return s1.length() - s2.length();
}
};
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet(lengthComparator);
treeSet.add("hi");
treeSet.add("hello");
treeSet.add("hey");
treeSet.add("haha");
treeSet.add("heihei");
treeSet.add("world");//没添加成功 因为world和hello一样长
treeSet.add("java");//没添加成功 因为java和haha一样长
System.out.println(treeSet);
//[hi, hey, haha, hello, heihei]
}
@Test
public void test4(){
//使用String类的定制比较器,按照字符串的长短,长度一样,再按内容比较大小
Comparator lengthComparator = new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
String s1 = (String) o1;
String s2 = (String) o2;
int result = s1.length() - s2.length();
if(result == 0){
return s1.compareTo(s2);
}
return result;
}
};
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet(lengthComparator);
treeSet.add("hi");
treeSet.add("hello");
treeSet.add("hey");
treeSet.add("haha");
treeSet.add("heihei");
treeSet.add("world");
treeSet.add("java");
System.out.println(treeSet);
//[hi, hey, haha, java, hello, world, heihei]
}
}
11.3 List集合
11.3.1 `List<E>`接口介绍
`java.util.List`接口继承自`Collection`接口,是单列集合的一个重要分支,习惯性地会将实现了`List`接口的对象称为List集合。
List的常用实现类有:`ArrayList`、`Vector`、`LinkedList`、`Stack`等。
- List集合所有的元素是以一种==线性方式==进行存储的
- 它是一个元素==存取有序==的集合。即元素的存入顺序和取出顺序有保证。
- 它是一个==带有索引==的集合,通过索引就可以精确的操作集合中的元素(与数组的索引是一个道理)。
- 集合中可以有==重复==的元素
这就像银行门口客服,给每一个来办理业务的客户分配序号:第一个来的是“张三”,客服给他分配的是0;第二个来的是“李四”,客服给他分配的1;以此类推,最后一个序号应该是“总人数-1”。
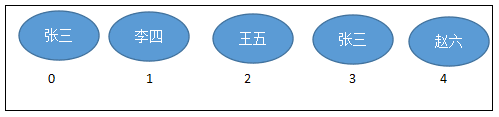
注意:
List集合关心元素是否有序,而不关心是否重复,请大家记住这个原则。例如“张三”可以领取两个号。
在JavaSE中`List`名称的类型有两个,一个是`java.util.List<E>`集合接口,一个是`java.awt.List`图形界面的组件,别导错包了。
11.3.2 ` List<E>`接口中常用方法
List作为Collection集合的子接口,不但继承了Collection接口中的全部方法,而且还增加了一些根据索引来操作集合元素的特有方法,如下:
1、添加元素
- `void add(int index, E ele)`:把元素添加到指定位置
- `boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> eles)`:把一组元素添加到指定位置
2、删除元素
- `E remove(int index)`:删除指定位置的元素
3、修改元素
- `E set(int index, E ele)`:替换[index]位置的元素
- `default void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator)`:按指定操作的要求替换元素
4、获取元素
- `E get(int index)`:返回[index]位置的元素
- `List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)`:返回[fromIndex, toIndex)范围的元素
- `int indexOf(Object obj)`:查询obj在列表中的位置,如果有重复,返回第1个
- `int lastIndexOf(Object obj)`:查询obj在列表中的地位,如果有重复,返回最后1个
5、其他方法
- `default void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) `:对List集合元素进行排序,如果想要通过元素的自然比较器排序,调用sort方法时传入null即可。
示例代码
package com.atguigu.list;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.UnaryOperator;
public class TestList {
@Test
public void test1(){
/*
ArrayList是List接口的实现类。
演示添加add
*/
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("hello");
list.add("java");
list.add(0,"atguigu");
list.add(2,"world");
System.out.println(list);//[atguigu, hello, world, java]
List<String> list2 = Arrays.asList("chai", "lin", "yan");
list.addAll(1,list2);
System.out.println(list);//[atguigu, chai, lin, yan, hello, world, java]
}
@Test
public void test2(){
/*
ArrayList是List接口的实现类。
演示删除remove(index)
*/
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("hello");
list.add("java");
list.remove(0);
System.out.println(list);
}
@Test
public void test3(){
/*
ArrayList是List接口的实现类。
演示删除
*/
List<Integer> list =new ArrayList<>();
list.add(10);
list.add(20);
list.add(30);
list.add(40);
list.remove(1);//删除[1]位置的元素
System.out.println(list);//[10, 30, 40]
//list.remove(30);//删除元素值为30的元素
list.remove(Integer.valueOf(30));//手动装箱
System.out.println(list);//[10, 40]
}
@Test
public void test4(){
/*
ArrayList是List接口的实现类。
演示修改替换
*/
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("hello");
list.add("java");
list.set(0,"hi");
System.out.println(list);//[hi, java]
UnaryOperator<String> u = new UnaryOperator<String>() {
@Override
public String apply(String s) {
return s.toUpperCase();
}
};
list.replaceAll(u);
System.out.println(list);//[HI, JAVA]
}
@Test
public void test5(){
/*
ArrayList是List接口的实现类.
演示查询,截取
*/
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("hello");
list.add("java");
list.add("world");
list.add("mysql");
list.add("java");
System.out.println(list.get(1));//java
System.out.println(list.indexOf("java"));//1
System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf("java"));//4
List<String> subList = list.subList(1, 3);//[1,3)下标范围的元素
System.out.println("subList = " + subList);//[java, world]
}
@Test
public void test6(){
//演示排序
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("hello");
list.add("java");
list.add("world");
list.add("mysql");
list.add("java");
System.out.println(list);
list.sort(null);
System.out.println(list);
Comparator<String> c = new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
return o1.length()-o2.length();
}
};
list.sort(c);
System.out.println(list);
}
}


